Lesson 11. Soil on Earth (Page 61)
- Students will appraise the value of soil based on the amount of fertile soil available on Earth
- Students will predict how not having access to healthy soil affects the people who live nearby
- Students can compare the health of soil in relation to plants to the consumption of healthy foods in relation to humans. (Unhealthy soil is low in minerals and can decrease yield and may sicken a plant. Humans too require vitamins and minerals to be healthy and if intake is low it causes humans to get sick and not have enough energy, etc…)

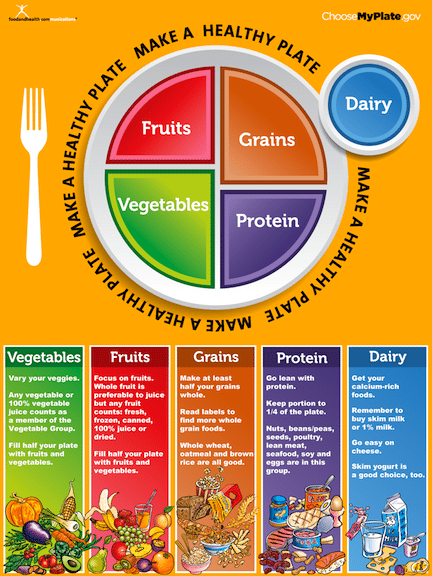
- Students can describe a balanced healthy diet (Myplate) and compare it to their description of healthy soil.
- Students can articulate the issues associated with limited healthy food access and provide solutions.
Core Curriculum Standards
Writing Standards: (W)
- 1.2-6.2: Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas and information clearly.
Speaking and Listening Standards: (SL)
- 1.4- 6.4: Report on a topic or text, or present an opinion.
- 1.1- 6.1: Participate in collaborative conversations with diverse partners about topics and texts with peers and adults in small and larger groups.
Language Standards: (L)
- 1.1-6.1: Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking.
NHES Pre-K-Grade 2
- 1.2.1: Identify that healthy behaviors impact personal health.
NHES Grades 3-5
- 1.5.1: Describe the relationship between healthy behaviors and personal health.
- 1.5.3: Describe ways in which safe and healthy school and community environments can promote personal health.
NHES Grades 6-8
- 1.8.1: Analyze the relationship between healthy behaviors and personal health.
Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS)
- MS-ESS3-3: Apply scientific principles to design a method for monitoring and minimizing a human impact on the environment.
- K-2-ETS1-1: Ask questions, make observations, and gather information about a situation people want to change to define a simple problem that can be solved through the development of a new or improved object or tool.
- K-2-ETS1-3: Analyze data from tests of two objects designed to solve the same problem to compare the strengths and weaknesses of how each performs.
- 3-5-ETS1-2: Generate and compare multiple possible solutions to a problem based on how well each is likely to meet the criteria and constraints of the problem.
- MS-ETS1-1: Define the criteria and constraints of a design problem with sufficient precision to ensure a successful solution, taking into account relevant scientific principles and potential impacts on people and the natural environment that may limit possible solutions.
- MS-ETS1-2: Evaluate competing design solutions using a systematic process to determine how well they meet the criteria and constraints of the problem.
